




Evaporative Condenser
The evaporative condenser is a common name for what is essentially a closed cooling tower. In fact, it *is* a closed cooling tower that uses the evaporation of sprayed water—carried away from the tower by air—to cool and exchange heat with the circulating medium inside the heat exchange tubes. Importantly, this circulating medium remains completely isolated from the external environment. Because the circulating medium is entirely enclosed and separated from the outside world, it’s sometimes referred to as an "evaporative condenser." Inside, the circulating medium is cooled only—there’s no consumption or evaporation involved. Meanwhile, as the spray water on the exterior of the heat exchange tubes evaporates, the resulting water vapor mixes extensively with the surrounding air, significantly increasing humidity levels. This saturated, high-humidity, high-environmental-airflow is then expelled from the tower into the external environment by an axial fan.
Key words:
Evaporative Condenser
Classification:

Hotline:
Evaporative Condenser
Overview
The evaporative condenser is a common name, also known as a closed cooling tower.
Actually, it's simply a closed cooling tower, which uses the evaporation of spray water—carried away from the tower by air—to cool and transfer heat to the circulating medium inside the heat exchange tubes. Notably, the circulating medium remains completely isolated from the external environment.
Because the cooled circulating medium is isolated from the outside environment and completely sealed, it is sometimes referred to as an evaporative condenser. The internal circulating medium undergoes only cooling—there is no consumption or evaporation involved.
After the spray water outside the heat exchange tubes vaporizes, the resulting large volume of water vapor mixes with air, increasing humidity. An axial fan then draws this saturated, high-humidity, high-enthalpy air out of the tower and into the surrounding environment.
Work process
► Latent heat of vaporization: Similar to closed cooling towers, it relies on the evaporation of spray water outside the heat exchange tubes, absorbing the latent heat of vaporization and carrying away the thermal energy from the industrial circulating water flowing inside the sealed heat exchange tubes.
► Plate heat exchange: Spray water and air are completely isolated from the circulating medium—there’s no direct contact whatsoever, only heat transfer occurs without any physical contact.
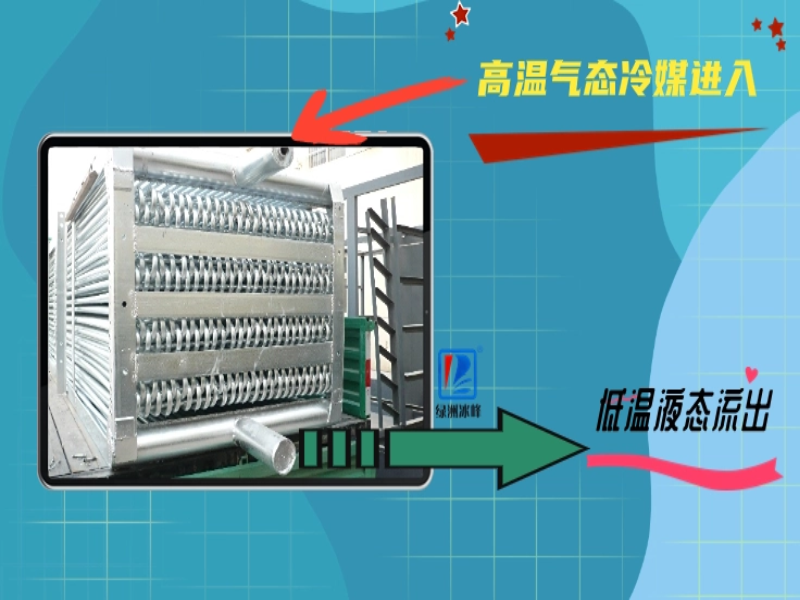
Main Advantages
► No Evaporation: It only cools—no evaporation, no consumption. The circulating medium is completely isolated from outside air, ensuring zero contact and preventing any evaporation, loss of medium, or contamination from entering. This guarantees the stability of the internal medium's composition.
► No scaling: Since there is no evaporation, the concentrations of scale-forming ions in the medium—such as calcium, magnesium, and sulfate—remain unchanged, preventing scaling from occurring.
► No algae is produced, offering excellent environmental performance;
► Save water, save electricity, and enjoy peace of mind—during winter and spring/autumn seasons, when temperatures are low, you may not even need to spray water; instead, air cooling alone can effectively meet cooling demands, resulting in significant water savings. It operates automatically, requiring no manual intervention—once the temperature reaches the preset level, the system will automatically stop the spray pump or fan.
Application scenarios
Commonly used in heavy industries such as iron and steel metallurgy, casting and smelting, petrochemicals, chemical fiber textiles, machinery, and power generation, it resists scaling and minimizes evaporation. It is often employed for cooling applications like desalinated water and purified water, operating within closed heat exchange tubes that are completely isolated from the external atmosphere.
► Steel metallurgy: blast furnaces, continuous casting and rolling, crystallizers, air compressors, and more;
► Large-scale casting: melting furnaces, frequency converters, quenching fluids, and more;
► Oil refining: reactors, smelting furnaces, heat exchangers, and more;
► Chemical Industry & Light Textiles: Reactors, etc.;
► Air conditioning cooling: compressor, etc.;
Add Sales Engineer Enterprise WeChat: Get Technical Copywriting for Free
Previous Page
Next Page
Previous Page
Next Page
Related Products
Leave us a message








